Key points:
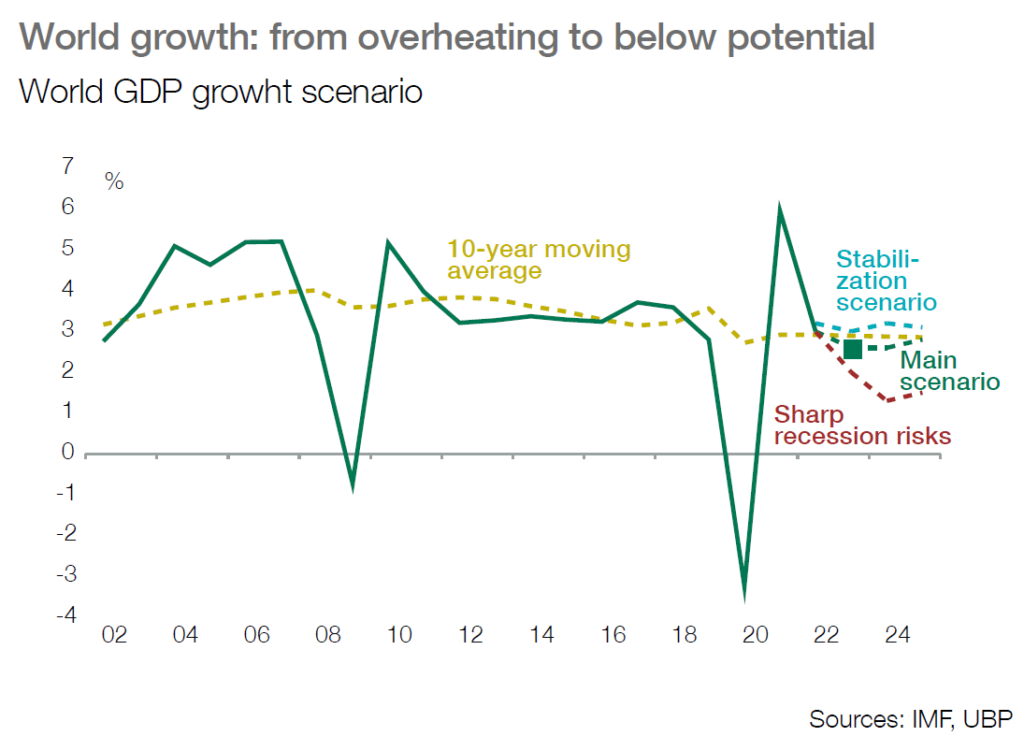
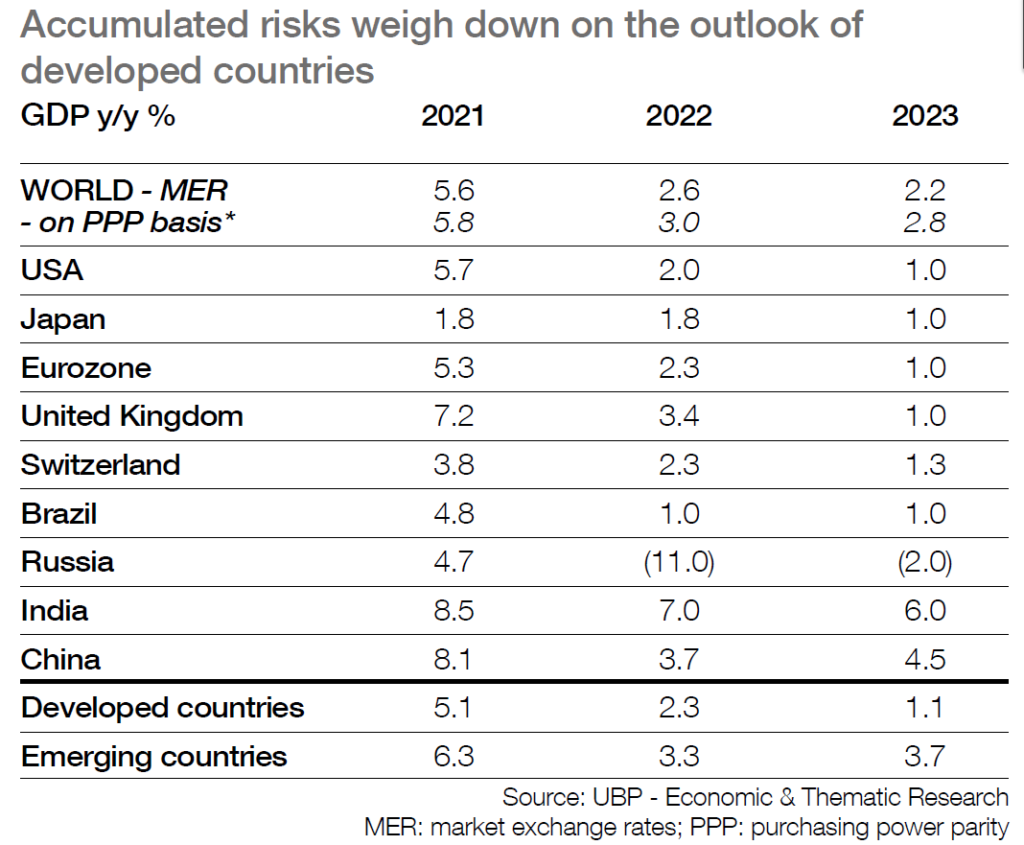
■ The 2023 scenario has been revised down for developed countries, facing accumulated risks and tighter monetary policy. The fight against inflation by central banks should drive domestic demand below potential from Q4-22, and a technical recession is forecast in early 2023.
■ This recession should be mild and limited but tail risks still exist: the Fed could hike rates too trongly and a full embargo of energy exports to Europe may generate deeper recession.
■ Inflation should progressively decline late in 2022 and significantly in 2023, but it will take time to get back to 2%.
■ Monetary policy will remain in restrictive mode over the next few months; the pace of adjustments in rates could be under review once key rates return to neutral or bove the neutral point.
Western countries to face below potential activity and rising recession risks
■ The US and European countries seem likely to face falling activity at year end and prospects of a technical recession have increased under the burden of high energy and geopolitical risks combined with tougher restrictive monetary
policy.
■ The eurozone looks most exposed to major downside risks as the constraints from energy could rise further entering the winter season. High inflation will depress consumers and shortages and bottlenecks will dampen industrial activity. The tougher ECB’s policy should weigh down on credit supply, with fragmentation risks on the rise within the area.
■ US domestic demand will slow down sharply as the Fed targets subdued growth and below otential activity to regain control on inflation; as a result, flat growth may be seen year end and a technical recession looks highly probable in early 2023.
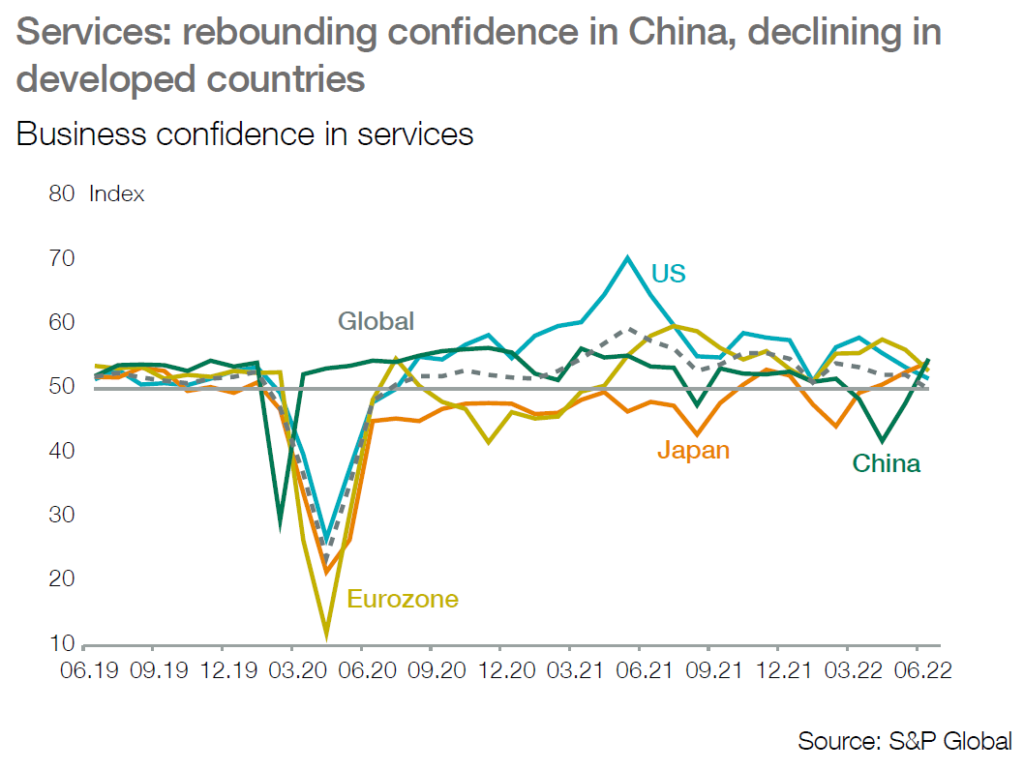
China: a progressive exit from recession is expected
■ Contrary to Western countries, China is expected progressively to recover in H2-22 after a recession in Q2. Firmer trend in industry and in consumption is expected with the combined renewed support of budgetary and monetary policy.